Welcome!
Welcome to the new CancerGRACE.org! Explore our fresh look and improved features—take a quick tour to see what’s new.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops in certain skin cells called melanocytes. These are the cells that make the pigment (melanin) that colors your skin. When exposed to UV radiation, such as sunlight, the melanocytes make more pigment, causing the skin to darken or tan.
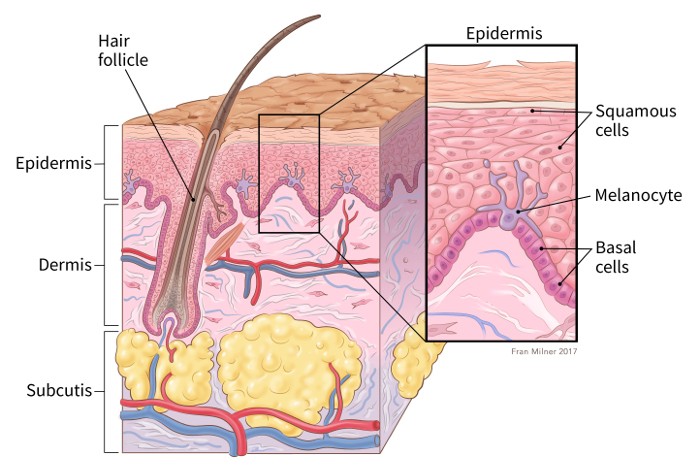
Your skin is your body’s largest organ, and it serves several important functions: protects your body from heat, injury and infection; stores water and fat; helps maintain body temperature; and makes vitamin D. The skin consists of two main layers:
Under the dermis lies the subcutis or hypodermis. This layer is not part of the skin, but connects the skin to muscles and bones. It consists of collagen and fat cells that conserve body heat and act as a shock absorber to protect organs from injury.
A mole is merely a cluster of melanocytes and surrounding skin tissue. They may be raised or flat, and may appear pink, brown, tan or similar to normal skin color. Common moles tend to be smaller than a pencil eraser. Melanoma can develop either from an existing mole or appear as a new mole, when the melanocytes become malignant. Melanoma can develop anywhere melanocytes are found, including the eye (ocular melanoma), digestive tract and lymph nodes, although these sites are less common.
Melanoma is less common than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers, and accounts for only 5 percent of all skin cancers. But it is the most serious skin cancer type and causes the majority of skin cancer deaths. Melanoma is more likely to spread to lymph nodes and other parts of the body, and form new tumors. It occurs most commonly in the trunk, between the shoulders and hips, on the head, neck, and in women, on the lower legs. Although rare in black people or others with dark skin, when melanoma does develop in people with darker skin types, it tends to occur on the palms and soles.
The number of melanoma cases has increased for the past 30 years, especially among young adults. During these decades, melanoma rates have increased 64 percent among white men and 153 percent among white women. Melanoma is now the most common cancer among people age 25 to 29. Indoor tanning is an important risk factor.
Melanomas fall into one of four different types:
A risk factor is anything that may increase your risk for a disease. Risk factors for melanoma include:
4487.jpg?itok=LooO274g)
Welcome to the new CancerGRACE.org! Explore our fresh look and improved features—take a quick tour to see what’s new.